5 things that can go wrong with your IUD and what to do about it.
 May 19, 2018
May 19, 2018
Cold and Flu
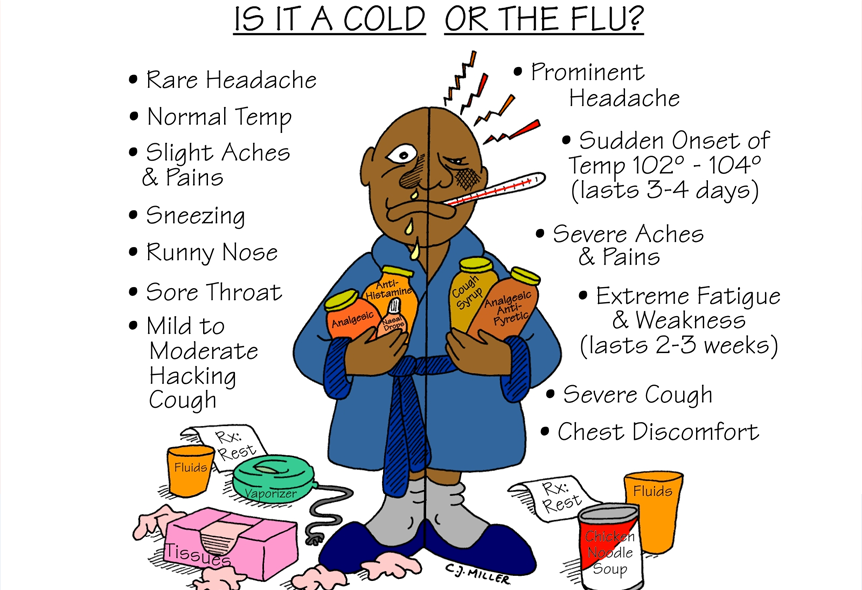
Many people think that the common cold and the flu are one in the same. While both are respiratory illnesses caused by viruses, the common cold and the flu are caused by very different viruses and they can also ultimately lead to very different results. Both being respiratory illness however, the common cold and the flu often present with very similar symptoms. It is for this reason that many people sometimes find it difficult to tell them apart.
The common cold is a viral infection that only affects the upper airway, meaning the throat and the nose. While a common cold can make you feel miserable, it’s usually harmless. The flu, also known as Influenza is a respiratory illness that can affect both the upper respiratory tract (i.e. the nose and throat) along with the lower respiratory tract (i.e. the airways and the lungs). The flu, which is extremely contagious, generally has symptoms that are more severe than those of a common cold. The flu can also be associated with serious, even life-threatening complications.
Although the common cold and flu are two different illnesses, they come with many of the same risk factors. Risk factors for contracting both a common cold or the flu include:

Cold and Flu causing airborne droplets
• Having a Weakened Immune System – If you have a chronic illness or are suffering from any disease that adversely affects your immune system, you have a higher risk of contracting a cold or the flu. Certain drugs, including those used to treated auto-immune diseases like Lupus and Psoriasis, anti-rejection drugs taken after organ transplant and drugs used to treat cancer all can weaken the immune system.
• Exposure – Being around people that have a cold or the flu is a major risk factor for contracting cold and flu. The viruses that cause cold and flu are airborne viruses. People with the infections, while coughing and sneezing, emit the virus particles into the air. Those around them can then inhale those particles, causing them to contract the illnesses.
• Age – Children and Senior Citizens are at an increased risk for contracting both the common cold and the flu. Older adult’s immune systems tend to be weaker than those of younger adults. And children, particularly those children who are in a daycare or school setting are at an increased risk for being in close contact with other people that have a cold or the flu.
• Chronic Illness – Multiple chronic conditions, including heart disease, congestive heart failure, asthma, and diabetes can increase a person’s risk of cold and flu. Having these conditions can also increase a flu sufferer’s chances of suffering complications from the flu.
• Pregnancy – The immune systems of women who are pregnant tend to be slightly compromised. This puts them at higher risk for both contracting a common cold or the flu, and for suffering major complications from the flu.
The viruses that cause the common cold include Rhinovirus, Human parainfluenza virus, Metapneumovirus, Coronaviruses, Adenovirus, Human respiratory syncytial virus and Enteroviruses. Those that cause the flu include Influenza A, Influenza B and Influenza C. Cold and flu viruses are spread from person to person by small droplets that float around in the air. When someone with a cold or the flu talks, coughs, clears their throat or sneezes, they can emit these small droplets into the air. People who are around them can then inhale them and contract the cold or the flu. Colds and the flu can also be spread from person to person by hand-to-hand contact, or by people with a cold or with the flu sharing contaminated items like telephones, towels, toys, or eating utensils.
 Symptoms of the common cold generally appear within one to three days of having been exposed to one of the viruses that can cause a cold. Because colds are generally limited to the upper respiratory tract, many symptoms of a cold also tend to involve the upper respiratory tract as well. They can include:
Symptoms of the common cold generally appear within one to three days of having been exposed to one of the viruses that can cause a cold. Because colds are generally limited to the upper respiratory tract, many symptoms of a cold also tend to involve the upper respiratory tract as well. They can include:
• Sore throat 
• Congestion
• Stuffy or runny nose
• Low-grade fever
• Cough
• Malaise (felling generally unwell)
• Mild headache
• Sneezing
Symptoms of the flu generally appear within one to four days of having been exposed to the flu. Flu symptoms can, at the beginning of a flu infection, resemble those of the common cold. A sore throat, runny nose, and sneezing are all common. However, while colds generally develop slowly, the flu usually hits you suddenly. As symptoms then worsen, flu symptoms can include:
• Aching muscles, particularly in the legs, arms, and back
• Headache
• Sore throat
• Sweats and chills
• Weakness and fatigue
• Persistent, dry cough
• Nasal congestion
• Fever that is over 100.4
• Shortness of breath
By and large, especially for healthy young people, colds and flu present very little risk of long-term danger. The flu being more aggressive than the common cold however is more likely to lead to complications. Complications of common cold and flu can include:
• Asthma attacks/exacerbations in Asthma sufferers.
• Bronchitis (i.e. inflammation and/or infection of the airways)
• Tonsillitis (i.e. inflammation and/or infection of the tonsils)
• Otitis Media (i.e. ear infections)
• Pneumonia (i.e. lung infection)
• Worsening of diabetes and resulting difficulty in controlling blood sugars.
• Worsening of congestive heart failure
• Worsening of preexisting lung diseases like Emphysema and Chronic Bronchitis.
• Death
There are a number of things that people can do to lessen their chances of getting both the common cold or the flu. They include the following:

In most cases, the presence of cold symptoms is enough for a Doctor to diagnose a cold. If a Doctor is concerned that complications from a cold might also be present, they may order a chest x-ray to evaluate the lungs and blood work to determine if other organs like the heart or kidneys have been adversely affected.
There are a number of tests available for diagnosing the flu. All of them test for the presence of the flu virus(es) in either the nose or the mouth. They involve sweeping a cotton swab across the back of the throat or the nose, and then sending that swab to a lab to test for the presences of the virus in either the oral or the nasal secretions. If the virus is detected, the results are “positive”. Depending on the test done, results can come back within 10 minutes to a few hours. The more rapid tests however are a little less accurate than those that take longer.
There is currently no cure for the common cold. While some people think that antibiotics treat the common cold, antibiotics treat bacterial infections. The common cold is caused by a viral infection. Treatment of a cold is therefore largely supportive. This means that cold sufferers should treat their symptoms while waiting for the infection to run its course. This includes use of the following:
• Pain Relievers like Acetaminophen and Ibuprofen can be used to treat and prevent both pain and fever. 
• Decongestants can be used to treat nasal congestion.
• Lozenges can be used to treat sore throats.
• Cough Suppressants like Dextromethorphan can be used to prevent cough.
• Aggressive hydration can be used to treat and prevent dehydration.
• Rest
There is currently no cure for the flu. Again, while some people think that antibiotics treat the flu, antibiotics treat bacterial infections. The flu is caused by a viral infection. Occasionally though, if the flu leads to a secondary bacterial infection (i.e. Pneumonia, Sinusitis, Tonsillitis, etc.), then antibiotics may be used. Much like the treatment of a cold, the treatment of the flu is largely supportive and can include the following:
• Pain Relivers like Acetaminophen and Ibuprofen can be used to treat and prevent both pain and fever.
• Decongestants can be used to treat nasal congestion.
• Lozenges can be used to treat sore throats.
• Cough Suppressants like Dextromethorphan can be used to prevent cough.
• Aggressive hydration can be used to treat and prevent dehydration.
• Rest
In addition to the use of supportive care to treat the flu, antiviral medications can also be used to treat the infection. These medications, while not cures for the flu, can shorten by 24-48 hours the time that a flu sufferer has the flu. Antiviral medications can also lower a flu sufferer’s risk for flu related complications like pneumonia and they include the following:
