5 things that can go wrong with your IUD and what to do about it.
 May 19, 2018
May 19, 2018

Diabetes
Diabetes is a disease that results when there is too much of a sugar called glucose in the blood. The most common types of diabetes are Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes. Currently, close to 10% of the world’s population suffers from diabetes. Given its prevalence, diabetes and diabetes related complications are the 6th most common cause of death worldwide.
Type 1 diabetes is also known by the names Juvenile Diabetes and Insulin Dependent Diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is caused when a person’s immune system damages to portions of their pancreas that are responsible for Insulin production. Insulin is a hormone that helps to move sugar from the blood stream into the body’s tissues. When Insulin levels are low, sugar cannot be effectively moved from the blood stream into the body’s tissues. Sugar then builds up in the blood stream causing “high blood sugar” levels. Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition. There is currently no cure for type 1 diabetes currently.
Type 2 diabetes is also known by the names Adult Onset Diabetes and Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes. Unlike type 1 diabetes, in type 2 diabetes the pancreas is typically able to make sufficient amounts of Insulin. However, in type 2 diabetes, the body is not able to properly utilize the Insulin that is produced by the pancreas. When the body is not able to properly utilize Insulin to move sugar from the blood stream into the body’s tissues, high blood sugar levels result. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition for most people. Some people are however able to reverse type 2 diabetes with healthy lifestyle changes.
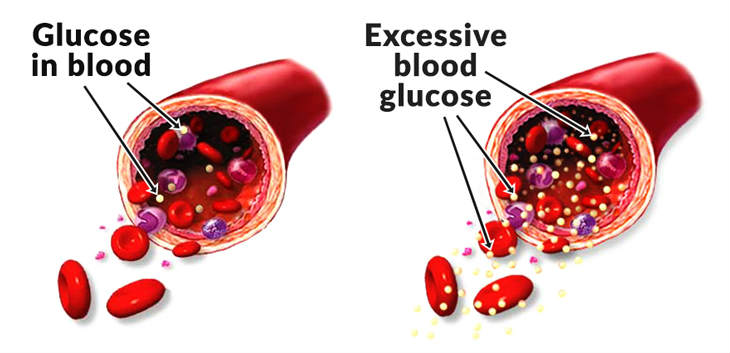
Normal blood sugar (left) and high blood sugar (right)
Gestational Diabetes is a form of diabetes seen only in pregnant women. In all pregnant women, the placenta produces a number of hormones that are critical to maintaining a healthy pregnancy. It is thought that some of these hormones affect the way that some women’s bodies processes Insulin. In these women, Insulin is not able to effectively do its job of moving sugar from the blood stream into the body’s tissues. High blood sugar levels then result. Gestational diabetes resolves when a pregnancy is finished. However, close to 50% of women who suffer gestational diabetes during a pregnancy will develop type 1 or type 2 diabetes later in life.

Gestational Diabetes

Heart Attack
Diabetes is dangerous because high blood sugar levels damage blood vessels. When blood vessels are damaged, blood does not flow through them optimally. When blood flow through damaged blood vessels is compromised, the organs that the damaged vessels provide blood to can also become damaged. In uncontrolled diabetes, the blood vessels supplying blood to the brain, heart, kidneys, nerves and eyes are all frequently damaged. Damage to the blood vessels supplying the brain can cause strokes. Damage to the blood vessels supplying the heart can cause heart attacks. So, it is not surprising that adults with diabetes are at a 200%-400% increased risk for heart attack and stroke.
when the blood vessels supplying the kidneys are damaged by high blood sugar levels, kidney damage and ultimately kidney failure can result. When the blood vessels supplying nerves are damaged, diabetes sufferers can experience the loss of sensation in their fingers and toes. When the blood vessels supplying the eyes are damaged, vision loss and blindness can result.
Common symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, frequent hunger, fatigue, blurry vision, weight gain or weight loss and poor wound healing.
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can be diagnosed using a variety of different blood tests.
Gestational diabetes can be diagnosed using either a glucose challenge test or a glucose tolerance tests.

Sugar (Glucose) Drinks

Regular exercise can both prevent and treat certain forms of diabetes.
There is no known way to prevent type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that results from the immune system attacking the pancreas. Complications from type 1 diabetes can however be delayed or prevented by adequately controlling blood sugar levels.
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent type 2 diabetes. They include;

Ideal Diabetic Diet
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent gestational diabetes. They include;
Just like maintaining a heathy weight, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, avoiding tobacco and getting enough sleep can help to prevent type 2 and gestational diabetes, so too can these healthy lifestyle modifications help to treat type 2 and gestational diabetes. When these lifestyle modifications are not able to bring blood sugar down adequately however, medications may be needed.
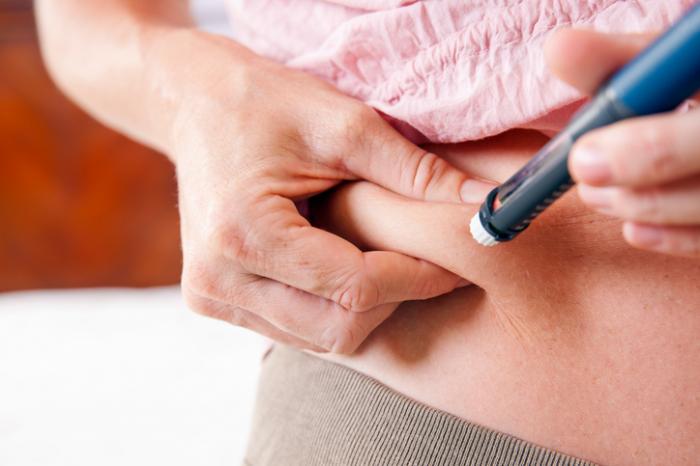
Insulin Injection
Type 1 diabetes results from a decreased production of Insulin by the pancreas. The treatment for type 1 diabetes therefore largely involves replacing the Insulin not being produced by the pancreas. Insulin is frequently replaced by injecting a synthetic form of it beneath the skin one or more times a day.
Type 2 diabetes primarily results when the body can not properly utilize the Insulin that the pancreas is producing. So, the treatment of type 2 diabetes typically involves taking oral medications that help the body to better utilize Insulin. When Insulin is better utilized, it is then able to do it’s job of helping to move sugar from the blood stream into the body’s tissues. Medications frequently used to treat type 2 diabetes include, Metformin, Sulfonylureas, Meglitinides, Thiazolidinediones, DPP-4 Inhibitors, SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Insulin can also be used sometimes to treat type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is frequently treated using Insulin, Metformin or the Sulfonylurea medication Glyburide.
